- Visual Studio 2019 Reactjs
- Visual Studio 2019 React Tutorial
- Visual Studio 2019 React Typescript
- Visual Studio 2019 React App
- Visual Studio 2019 React Native
- Visual Studio Create React App
Visual Studio allows you to easily create a Node.js project and experience IntelliSense and other built-in features that support Node.js. In this tutorial for Visual Studio, you create a Node.js web application project from a Visual Studio template. Then, you create a simple app using React.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Download the Visual studio 2019 community edition. When selecting the options, be sure to at least include Desktop development with C; Ensure you have started visual studio at least once, and you are able to create a working c project. To validate this, choose Create a new project, choose Console App, and use all default options.
- I have followed the steps outlined in this so post, and have successfully created a React Application inside Visual Studio from the 'Blank Node.js Web Application'. Everything works except debugging from VS! I have also followed this Microsoft article here which describes exactly what I want to do!!! - It walks you through 'how to setup a react app in Visual Studio using the node web app.
- Create a Node.js project
- Add npm packages
- Add React code to your app
- Transpile JSX
- Attach the debugger
For this tutorial we'll be using Visual Studio 2019. If you do not already have a copy of Visual Studio, the Community version is free. We will be using ASP.NET Core MVC. Click the 'Browse' tab, search for 'React.AspNet', and install the React.AspNet package. Install a JS engine # While we're managing NuGet packages, we need to install a JS. Crudreactvisualstudioc-crud com react visual studio 2019 c#. Using React in Visual Studio Code React is a popular JavaScript library developed by Facebook for building web application user interfaces. The Visual Studio Code editor supports React.js IntelliSense and code navigation out of the box. Welcome to React #.
Before you begin

Here's a quick FAQ to introduce you to some key concepts.
What is Node.js?
Node.js is a server-side JavaScript runtime environment that executes JavaScript server-side.
What is npm?
npm is the default package manager for the Node.js. The package manager makes it easier for programmers to publish and share source code of Node.js libraries and is designed to simplify installation, updating, and uninstallation of libraries.
What is React?
React is a front-end framework to create a UI.
What is JSX?
JSX is a JavaScript syntax extension, typically used with React to describe UI elements. JSX code must be transpiled to plain JavaScript before it can run in a browser.
What is webpack?
webpack bundles JavaScript files so they can run in a browser. It can also transform or package other resources and assets. It is often used to specify a compiler, such as Babel or TypeScript, to transpile JSX or TypeScript code to plain JavaScript.
Prerequisites
You must have Visual Studio installed and the Node.js development workload.
If you haven't already installed Visual Studio 2019, go to the Visual Studio downloads page to install it for free.
If you haven't already installed Visual Studio 2017, go to the Visual Studio downloads page to install it for free.
If you need to install the workload but already have Visual Studio, go to Tools > Get Tools and Features.., which opens the Visual Studio Installer. Choose the Node.js development workload, then choose Modify.
You must have the Node.js runtime installed.
This tutorial was tested with version 12.6.2.
If you don't have it installed, we recommend you install the LTS version from the Node.js website for best compatibility with outside frameworks and libraries. Node.js is built for 32-bit and 64-bit architectures. The Node.js tools in Visual Studio, included in the Node.js workload, support both versions. Only one is required and the Node.js installer only supports one being installed at a time.
In general, Visual Studio automatically detects the installed Node.js runtime. If it does not detect an installed runtime, you can configure your project to reference the installed runtime in the properties page (after you create a project, right-click the project node, choose Properties, and set the Node.exe path). You can use a global installation of Node.js or you can specify the path to a local interpreter in each of your Node.js projects.
Create a project
First, create a Node.js web application project.
Open Visual Studio.
Create a new project.
Press Esc to close the start window. Type Ctrl + Q to open the search box, type Node.js, then choose Blank Node.js Web Application - JavaScript. (Although this tutorial uses the TypeScript compiler, the steps require that you start with the JavaScript template.)
In the dialog box that appears, choose Create.
From the top menu bar, choose File > New > Project. In the left pane of the New Project dialog box, expand JavaScript, then choose Node.js. In the middle pane, choose Blank Node.js Web Application, type the name NodejsWebAppBlank, then choose OK.
If you don't see the Blank Node.js Web Application project template, you must add the Node.js development workload. For detailed instructions, see the Prerequisites.
Visual Studio creates the new solution and opens your project.
(1) Highlighted in bold is your project, using the name you gave in the New Project dialog box. In the file system, this project is represented by a .njsproj file in your project folder. You can set properties and environment variables associated with the project by right-clicking the project and choosing Properties. You can do round-tripping with other development tools, because the project file does not make custom changes to the Node.js project source.
(2) At the top level is a solution, which by default has the same name as your project. A solution, represented by a .sln file on disk, is a container for one or more related projects.
(3) The npm node shows any installed npm packages. You can right-click the npm node to search for and install npm packages using a dialog box or install and update packages using the settings in package.json and right-click options in the npm node.
(4) package.json is a file used by npm to manage package dependencies and package versions for locally-installed packages. For more information, see Manage npm packages.
(5) Project files such as server.js show up under the project node. server.js is the project startup file and that is why it shows up in bold. You can set the startup file by right-clicking a file in the project and selecting Set as Node.js startup file.
Add npm packages
This app requires a number of npm modules to run correctly.
- react
- react-dom
- express
- path
- ts-loader
- typescript
- webpack
- webpack-cli
In Solution Explorer (right pane), right-click the npm node in the project and choose Install New npm Packages.
In the Install New npm Packages dialog box, you can choose to install the most current package version or specify a version. If you choose to install the current version of these packages, but run into unexpected errors later, you may want to install the exact package versions described later in these steps.
In the Install New npm Packages dialog box, search for the react package, and select Install Package to install it.
Select the Output window to see progress on installing the package (select Npm in the Show output from field). When installed, the package appears under the npm node.
The project's package.json file is updated with the new package information including the package version.
Instead of using the UI to search for and add the rest of the packages one at a time, paste the following code into package.json. To do this, add a
dependenciessection with this code:If there is already a
dependenciessection in your version of the blank template, just replace it with the preceding JSON code. For more information on use of this file, see package.json configuration.Save the changes.
Right-click npm node in your project and choose Install npm Packages.
This command runs the npm install command directly.
In the lower pane, select the Output window to see progress on installing the packages. Installation may take a few minutes and you may not see results immediately. To see the output, make sure that you select Npm in the Show output from field in the Output window.
Here are the npm modules as they appear in Solution Explorer after they are installed.
Note
If you prefer to install npm packages using the command line, right-click the project node and choose Open Command Prompt Here. Use standard Node.js commands to install packages.
Add project files
In these steps, you add four new files to your project.
- app.tsx
- webpack-config.js
- index.html
- tsconfig.json
For this simple app, you add the new project files in the project root. (In most apps, you typically add the files to subfolders and adjust relative path references accordingly.)
In Solution Explorer, right-click the project NodejsWebAppBlank and choose Add > New Item.
In the Add New Item dialog box, choose TypeScript JSX file, type the name app.tsx, and select Add or OK.
Repeat these steps to add webpack-config.js. Instead of a TypeScript JSX file, choose JavaScript file.
Repeat the same steps to add index.html to the project. Instead of a JavaScript file, choose HTML file.
Repeat the same steps to add tsconfig.json to the project. Instead of a JavaScript file, choose TypeScript JSON Configuration file.
Add app code
Open server.js and replace the existing code with the following code:
The preceding code uses Express to start Node.js as your web application server. This code sets the port to the port number configured in the project properties (by default, the port is configured to 1337 in the properties). To open the project properties, right-click the project in Solution Explorer and choose Properties.
Open app.tsx and add the following code:
The preceding code uses JSX syntax and React to display a simple message.
Open index.html and replace the body section with the following code:
This HTML page loads app-bundle.js, which contains the JSX and React code transpiled to plain JavaScript. Currently, app-bundle.js is an empty file. In the next section, you configure options to transpile the code.
Configure webpack and TypeScript compiler options
In the previous steps, you added webpack-config.js to the project. Next, you add webpack configuration code. You will add a simple webpack configuration that specifies an input file (app.tsx) and an output file (app-bundle.js) for bundling and transpiling JSX to plain JavaScript. For transpiling, you also configure some TypeScript compiler options. This code is a basic configuration that is intended as an introduction to webpack and the TypeScript compiler.
In Solution Explorer, open webpack-config.js and add the following code.
The webpack configuration code instructs webpack to use the TypeScript loader to transpile the JSX.
Open tsconfig.json and replace the default code with the following code, which specifies the TypeScript compiler options:
app.tsx is specified as the source file.
Transpile the JSX
In Solution Explorer, right-click the project node and choose Open Command Prompt Here.
In the command prompt, type the following command:
node_modules.binwebpack app.tsx --config webpack-config.jsThe command prompt window shows the result.
If you see any errors instead of the preceding output, you must resolve them before your app will work. If your npm package versions are different than the versions shown in this tutorial, that can be a source of errors. One way to fix errors is to use the exact versions shown in the earlier steps. Also, if one or more of these package versions has been deprecated and results in an error, you may need to install a more recent version to fix errors. For information on using package.json to control npm package versions, see package.json configuration.
In Solution Explorer, right-click the project node and choose Add > Existing Folder, then choose the dist folder and choose Select Folder.
Visual Studio adds the dist folder to the project, which contains app-bundle.js and app-bundle.js.map.
Open app-bundle.js to see the transpiled JavaScript code.
If prompted to reload externally modified files, select Yes to All.
Each time you make changes to app.tsx, you must rerun the webpack command. To automate this step, add a build script to transpile the JSX.
Add a build script to transpile the JSX
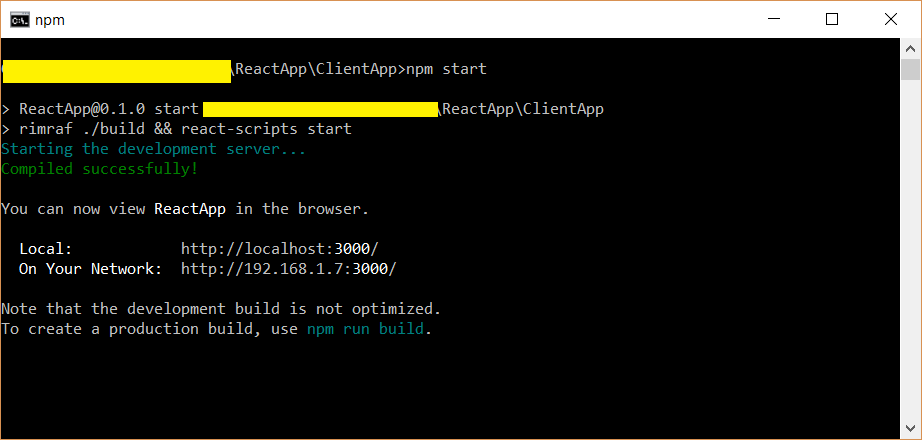
Starting in Visual Studio 2019, a build script is required. Instead of transpiling JSX at the command line (as shown in the preceding section), you can transpile JSX when building from Visual Studio.
Open package.json and add the following section after the
dependenciessection:
Run the app
Select either Web Server (Google Chrome) or Web Server (Microsoft Edge) as the current debug target.
If Chrome is available on your machine, but does not show up as an option, choose Browse With from the debug target dropdown list, and select Chrome as the default browser target (choose Set as Default).
To run the app, press F5 (Debug > Start Debugging) or the green arrow button.
A Node.js console window opens that shows the port on which the debugger is listening.
Visual Studio starts the app by launching the startup file, server.js.
Close the browser window.
Close the console window.
Set a breakpoint and run the app
In server.js, click in the gutter to the left of the
staticPathdeclaration to set a breakpoint:Breakpoints are the most basic and essential feature of reliable debugging. A breakpoint indicates where Visual Studio should suspend your running code so you can take a look at the values of variables, or the behavior of memory, or whether or not a branch of code is getting run.
To run the app, press F5 (Debug > Start Debugging).
The debugger pauses at the breakpoint you set (the current statement is marked in yellow). Now, you can inspect your app state by hovering over variables that are currently in scope, using debugger windows like the Locals and Watch windows.
Press F5 to continue the app.
If you want to use the Chrome Developer Tools or F12 Tools for Microsoft Edge, press F12. You can use these tools to examine the DOM and interact with the app using the JavaScript Console.
Close the web browser and the console.
Set and hit a breakpoint in the client-side React code
In the preceding section, you attached the debugger to server-side Node.js code. To attach the debugger from Visual Studio and hit breakpoints in client-side React code, the debugger needs help to identify the correct process. Here is one way to enable this.
Prepare the browser for debugging
For this scenario, use either Microsoft Edge (Chromium), currently named Microsoft Edge Beta in the IDE, or Chrome.
Close all windows for the target browser.
Other browser instances can prevent the browser from opening with debugging enabled. (Browser extensions may be running and preventing full debug mode, so you may need to open Task Manager to find unexpected instances of Chrome.)
For Microsoft Edge (Chromium), also shut down all instances of Chrome. Because both browsers share the chromium code base, this gives the best results.
Start your browser with debugging enabled.
Starting in Visual Studio 2019, you can set the
--remote-debugging-port=9222flag at browser launch by selecting Browse With.. > from the Debug toolbar, then choosing Add, and then setting the flag in the Arguments field. Use a different friendly name for the browser such as Edge with Debugging or Chrome with Debugging. For details, see the Release Notes.Alternatively, open the Run command from the Windows Start button (right-click and choose Run), and enter the following command:
msedge --remote-debugging-port=9222or,
chrome.exe --remote-debugging-port=9222Open the Run command from the Windows Start button (right-click and choose Run), and enter the following command:
chrome.exe --remote-debugging-port=9222This starts your browser with debugging enabled.
The app is not yet running, so you get an empty browser page.
Attach the debugger to client-side script
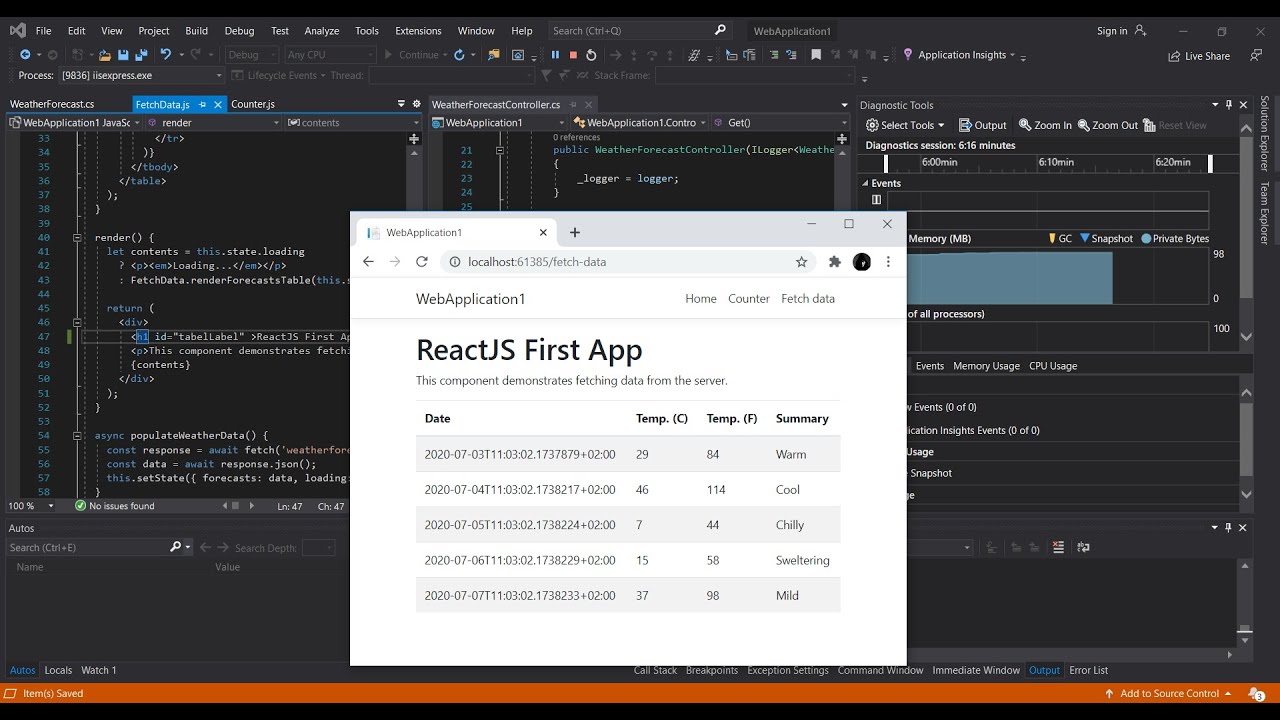
Switch to Visual Studio and then set a breakpoint in your source code, either app-bundle.js or app.tsx.
For app-bundle.js, set the breakpoint in the
render()function as shown in the following illustration:To find the
render()function in the transpiled app-bundle.js file, use Ctrl+F (Edit > Find and Replace > Quick Find).For app.tsx, set the breakpoint inside the
render()function, on thereturnstatement.If you are setting the breakpoint in the .tsx file (rather than app-bundle.js), you need to update webpack-config.js. Replace the following code:
with this code:
This is a development-only setting to enable debugging in Visual Studio. This setting allows you to override the generated references in the source map file, app-bundle.js.map, when building the app. By default, webpack references in the source map file include the webpack:/// prefix, which prevents Visual Studio from finding the source file, app.tsx. Specifically, when you make this change, the reference to the source file, app.tsx, gets changed from webpack:///./app.tsx to ./app.tsx, which enables debugging.
Select your target browser as the debug target in Visual Studio, then press Ctrl+F5 (Debug > Start Without Debugging) to run the app in the browser.
If you created a browser configuration with a friendly name, choose that as your debug target.
The app opens in a new browser tab.
Choose Debug > Attach to Process.
Tip
Starting in Visual Studio 2017, once you attach to the process the first time by following these steps, you can quickly reattach to the same process by choosing Debug > Reattach to Process.
In the Attach to Process dialog box, get a filtered list of browser instances that you can attach to.
In Visual Studio 2019, choose the correct debugger for your target browser, JavaScript (Chrome) or JavaScript (Microsoft Edge - Chromium) in the Attach to field, type chrome or edge in the filter box to filter the search results.
In Visual Studio 2017, choose Webkit code in the Attach to field, type chrome in the filter box to filter the search results.
Select the browser process with the correct host port (localhost in this example), and select Attach. Hp tapedrive driver.
The port (1337) may also appear in the Title field to help you select the correct browser instance.
The following example shows how this looks for the Microsoft Edge (Chromium) browser.
You know the debugger has attached correctly when the DOM Explorer and the JavaScript Console open in Visual Studio. These debugging tools are similar to Chrome Developer Tools and F12 Tools for Microsoft Edge.
Tip
If the debugger does not attach and you see the message 'Unable to attach to the process. An operation is not legal in the current state.', use the Task Manager to close all instances of the target browser before starting the browser in debugging mode. Browser extensions may be running and preventing full debug mode.
Because the code with the breakpoint already executed, refresh your browser page to hit the breakpoint.
While paused in the debugger, you can examine your app state by hovering over variables and using debugger windows. You can advance the debugger by stepping through code (F5, F10, and F11). For more information on basic debugging features, see First look at the debugger.
You may hit the breakpoint in either app-bundle.js or its mapped location in app.tsx, depending on which steps you followed previously, along with your environment and browser state. Either way, you can step through code and examine variables.
If you need to break into code in app.tsx and are unable to do it, use Attach to Process as described in the previous steps to attach the debugger. Make sure you that your environment is set up correctly:
You closed all browser instances, including Chrome extensions (using the Task Manager), so that you can run the browser in debug mode. Make sure you start the browser in debug mode.
Make sure that your source map file includes a reference to ./app.tsx and not webpack:///./app.tsx, which prevents the Visual Studio debugger from locating app.tsx.Alternatively, if you need to break into code in app.tsx and are unable to do it, try using the
debugger;statement in app.tsx, or set breakpoints in the Chrome Developer Tools (or F12 Tools for Microsoft Edge) instead.
If you need to break into code in app-bundle.js and are unable to do it, remove the source map file, app-bundle.js.map.
Next steps
-->The App Center SDK uses a modular architecture so you can use any or all of the services.
Let's get started with setting up App Center React Native SDK in your app to use App Center Analytics and App Center Crashes.
1. Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure that the following prerequisites are met:
- You're using a React Native project that runs React Native 0.34 or later.
- You're targeting devices that are running on Android Version 5.0/API level 21 or later, or iOS version 9.0 or later.
- You're not using any other library that provides Crash Reporting functionality on iOS.
- For iOS, the default way to use the SDK requires CocoaPods. (If you haven't installed CocoaPods, follow the CocoaPods Getting Started to do so). Nonetheless, it's possible to link the SDK manually.
2. Create your app in the App Center Portal to obtain the App Secret
If you've already created your app in the App Center portal, you can skip this step.
- Head over to appcenter.ms.
- Sign up or log in and hit the blue button on the top right corner of the portal that says Add new and select Add new app from the dropdown menu.
- Enter a name and an optional description for your app.
- Select the appropriate OS (Android or iOS) and select React Native as the platform.
- Hit the button at the bottom right that says Add new app.
Once you've created an app, you can obtain its App Secret on the Settings page on the App Center Portal. At the top right hand corner of the Settings page, click on the triple vertical dots and select Copy app secret to get your App Secret.
3. Add the App Center SDK modules
The default integration of the SDK uses CocoaPods for iOS. If you're not using CocoaPods in your app, you need to integrate the React Native SDK manually for your iOS app.
Open a Terminal and navigate to the root of your React Native project, then enter the following line to add App Center Analytics and Crashes to the app:
In case you prefer yarn over npm, use the following command to install App Center:
The App Center SDK uses a modular approach, where you just add the modules for App Center services that you want to use. appcenter-analytics and appcenter-crashes make sense to add to almost every app, as they provide value with no additional setup required. appcenter provides general purpose App Center APIs, useful for multiple services.
3.1 Integrate the SDK automatically for React Native 0.60
3.1.1 Integrate React Native iOS
Run
pod install --repo-updatefrom iOS directory to install CocoaPods dependencies.Create a new file with the name
AppCenter-Config.plistwith the following content and replace{APP_SECRET_VALUE}with your app secret value. Don't forget to add this file to the Xcode project (right-click the app in Xcode and click Add files to ..).Modify the app's AppDelegate.m file to include code for starting SDK:
- Add these lines to import section above the
#if DEBUGor#ifdef FB_SONARKIT_ENABLEDdeclaration (if present):
- Add these lines to the
didFinishLaunchingWithOptionsmethod
- Add these lines to import section above the
3.1.2 Integrate React Native Android
Visual Studio 2019 Reactjs
Create a new file with the name appcenter-config.json in
android/app/src/main/assets/with the following content and replace{APP_SECRET_VALUE}with your app secret value.
Note: If the folder named assets doesn't exist, it should be created under 'project_root/android/app/src/main/assets'
Modify the app's res/values/strings.xml to include the following lines:
3.2 Integrate the SDK automatically for React Native lower than 0.60
Note
If you have your React modules linked using relative path inside your Podfile but not referenced in the project, the linking script will fail because it links App Center using static pod versions. You either must follow the steps from the React Native troubleshooting section if you've already run the linking script, or link it yourself
Link the plugins to the React Native app by using the react-native link command.
For iOS, it will try to download the App Center SDK for iOS and macOS from CocoaPods, if you see an error like:
Run the following command:
And then retry running
react-native link.Note
App Center SDK doesn't set up mocks automatically for App Center modules during the linking process. If you're using Jest test framework in your application and experience errors caused by the App Center SDK while running tests with Jest, add the following to the jest section of package.json file (include only modules in use):
Note
Whether processing of crashes is automatic or triggered by Javascript methods, crashes are always processed after the restart of the application. Crashes can't be processed at the time the application crashes.
Edit the project's
android/app/src/main/assets/appcenter-config.jsonand replace theYOUR_APP_SECRETplaceholder value with your App Center project's application secret.Edit the project's
ios/{YourAppName}/AppCenter-Config.plistfile, and replace theYOUR_APP_SECRETplaceholder value with your App Center project's application secret. If AppCenter-Config.plist already exists but not part of your Xcode project, you must add it to the Xcode project manually (right-click the app in XCode and click Add files to ..).
3.3 [iOS only] Integrate the SDK manually for React Native without react-native link or CocoaPods
Do this integration, if you don't want to use CocoaPods.We strongly recommend integrating the SDK via CocoaPods as described above. Nonetheless, it's also possible to integrate the iOS native SDK manually.
Note
The latest App Center React Native SDK doesn't necessarily depend on the latest App Center iOS SDK, because the iOS SDK is updated and released before the React Native one.
The consequence is that you must know which version of the iOS SDK the React Native SDK depends on.
Download the App Center SDK for React Native frameworks provided as a zip file and unzip it.
You'll see a folder named AppCenterReactNativeShared which contains a single framework for the required React Native iOS bridge.
Download the corresponding App Center SDK for iOS frameworks provided as a zip file and unzip it.
You'll see a folder called AppCenter-SDK-Apple/iOS that contains different frameworks for each App Center service. The framework called
AppCenteris required in the project as it contains code that's shared between the different modules.[Optional] Create a subdirectory for 3rd-party libraries.
- As a best practice, 3rd-party libraries usually reside inside a subdirectory (it's often called Vendor), so if you don't have your project organized with a subdirectory for libraries, create a Vendor subdirectory now (under the ios directory of your project).
- Create a group called Vendor inside your Xcode project to mimic your file structure on disk.
Open Finder and copy the previously unzipped AppCenter-SDK-Apple/iOS and AppCenterReactNativeShared folders into your project's folder at the location where you want it to reside.
Add the SDK frameworks to the project in Xcode:
- Make sure the Project Navigator is visible (⌘+1).
- Drag and drop the AppCenter.framework, AppCenterAnalytics.framework, AppCenterCrashes.framework and AppCenterReactNativeShared.framework files from the Finder (in the location from the previous step) into Xcode's Project Navigator. The AppCenter.framework and AppCenterReactNativeShared.framework files are required to start the SDK, make sure they're added to your project, otherwise the other modules won't work and your app won't compile.
- A dialog will appear, make sure your app target is checked, then click Finish.
Link AppCenter React Native plugins projects to your app's project:
Make sure the Project Navigator is visible (⌘+1).
For each AppCenter React Native plugin navigate to the folder containing source code. Paths respectively will be
/node_modules/appcenter/ios/node_modules/appcenter-analytics/ios/node_modules/appcenter-crashes/ios/node_modules/appcenter-push/ios
Drag and drop
.xcodeprojfiles from the Finder into Xcode's Project Navigator. Typically under Libraries group.
Link libraries for AppCenter React Native plugins.Open your project settings and under General tab in the Linked Frameworks and Libraries section add new items referencing target libraries added on the previous step:
libAppCenterReactNative.alibAppCenterReactNativeAnalytics.alibAppCenterReactNativeCrashes.alibAppCenterReactNativePush.a
Modify Header Search Paths to find headers from the AppCenter React Native plugins projects.Open your project settings and under Build Settings tab in the Header Search Paths section add new locations for header files:
$(SRCROOT)/./node_modules/appcenter/ios/AppCenterReactNative$(SRCROOT)/./node_modules/appcenter-analytics/ios/AppCenterReactNativeAnalytics$(SRCROOT)/./node_modules/appcenter-crashes/ios/AppCenterReactNativeCrashes$(SRCROOT)/./node_modules/appcenter-push/ios/AppCenterReactNativePush
Modify the app's AppDelegate.m file to include code for starting SDK:
- Add these lines to import section above the
#if DEBUGor#ifdef FB_SONARKIT_ENABLEDdeclaration (if present):
- Add these lines to the
didFinishLaunchingWithOptionsmethod
- Add these lines to import section above the
Create new file with the name
AppCenter-Config.plistwith the following content and replace{APP_SECRET_VALUE}with your app secret value. Don't forget to add this file to the XCode project (right-click the app in XCode and click Add files to ..).
Note
The next two steps are only for the apps that use React Native 0.60 and above.
Disable autolinking for React Native 0.60 and above:
- Inside the node_modules folder in each App Center package open react-native.config.js and set
dependency.platforms.iostonull:
- Inside the node_modules folder in each App Center package open react-native.config.js and set
Modify Header Search Paths to find React Native headers from the App Center React Native plugins projects:
- Make sure the Project Navigator is visible (⌘+1).
- For each AppCenter React Native plugins project that you've added to the Libraries group in step 8:
- Select the project and under Build Settings tab in the Header Search Paths section add new locations for header files with a
recursiveoption:${SRCROOT}/./././ios/Pods/Headers
- Select the project and under Build Settings tab in the Header Search Paths section add new locations for header files with a
3.4 [Android only] Integrate the SDK manually for React Native lower than 0.60 without react-native link
Integration steps without the react-native link command.
Open android/settings.gradle file and insert the following lines. Include the dependencies that you want in your project. Each SDK module needs to be added as a separate dependency in this section. If you want to use App Center Analytics and Crashes, add the following lines:
Note
Due to termination of jCenter support all our assemblies were moved to the Maven Central repository. Please follow this guide about migration from jCenter to Maven Central.
Visual Studio 2019 React Tutorial
Open the project's app level build.gradle file (
android/app/build.gradle) and add the following lines intodependenciessection:Modify the app's MainApplication.java file to include code for starting SDK:
- Add these lines to the import section
- Add AppCenter packages to the
List<ReactPackage> getPackages()method
Open strings.xml file (
android/app/src/main/res/values) and add the following lines inside<resources></resources>tags:Create a new file with the name appcenter-config.json in
android/app/src/main/assets/with the following content and replaceAPP_SECRET_VALUEwith your app secret value.
3.5 If you use auto-backup to avoid getting incorrect information about device, follow the next steps:
Note
Apps that target Android 6.0 (API level 23) or higher have Auto Backup automatically enabled.
Note
If you already have a custom file with backup rule, switch to the third step.
a. Create appcenter_backup_rule.xml file in the android/app/src/main/res/xml folder.
b. Open the project's AndroidManifest.xml file. Add the android:fullBackupContent attribute to the <application> element. It should point to the appcenter_backup_rule.xml resource file.
Visual Studio 2019 React Typescript
c. Add the following backup rules to the appcenter_backup_rule.xml file:
4. Start the SDK
Now you can build and launch your application either from command line or Xcode/Android Studio.
4.1 Build and run your application from command line
You may build and launch your iOS application by the following command:
Tip
Visual Studio 2019 React App
You can launch it on an iOS simulator or iOS device by specifying the iOS device name in react-native run-ios --device 'myDeviceName'.
You may build and launch your Android application by the following command:
Tip
You can launch it on an android emulator or android device by specifying the device id in react-native run-android --deviceId 'myDeviceId' (deviceId from adb devices command).

Visual Studio 2019 React Native
4.2 Build and run your application from Xcode or Android Studio
For iOS, open your project's ios/{appname}.xcworkspace or ios/{appname}.xcodeproj file in Xcode and build from there.
Note
Visual Studio Create React App
If you linked App Center automatically via react-native link (as in step 3.1), you should open the project's ios/{appname}.xcworkspace file in Xcode. Because App Center CocoaPods dependencies only works with xcworkspace not xcodeproj, and the ios/{appname}.xcodeproj file won't have App Center CocoaPods dependencies linked.
For Android, import your android project in Android Studio and build from there.
You're all set to visualize Analytics and Crashes data on the portal that the SDK collects automatically. There's no additional setup required. Look at Analytics and Crashes section for APIs guides and walkthroughs to learn what App Center can do.
